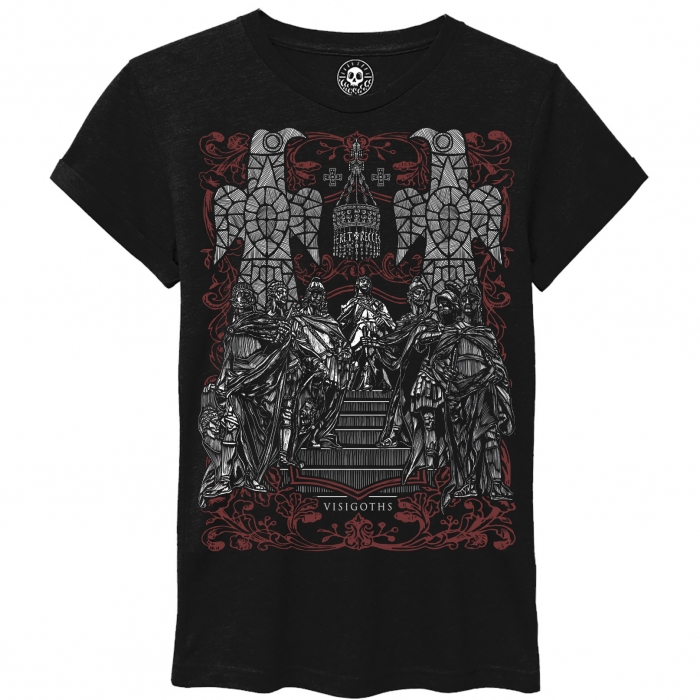
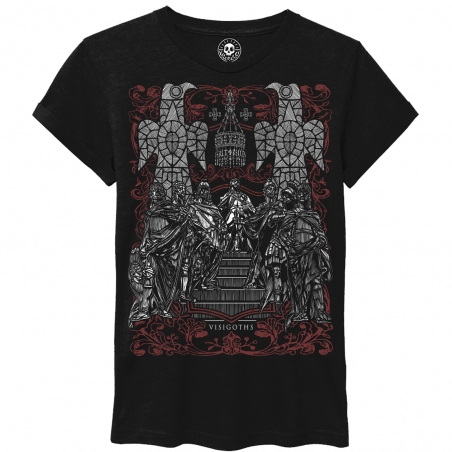
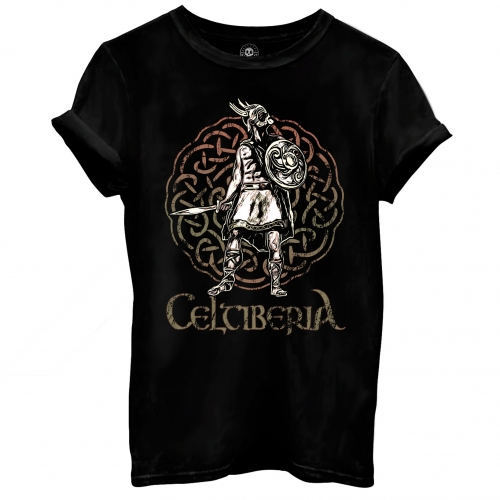
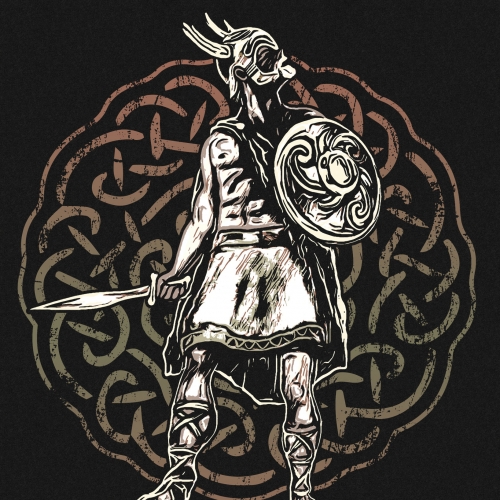
The fierce resistance against the invader of the pre-Roman peoples comes from afar. In the peninsula, the process concluded with the Cantabrian wars (19 BC), where in a bloody war the Romans fought against the Celtic peoples of the North (the Asturian and Cantabrian tribes). Iberia was the scene of wars of occupation, subjugation, strategic alliances, cultural assimilation, interests and betrayals from Carthage -Sagunto- and subsequent rebellions, in the development of Romanization, such as the ilergetes and Iberians (submitted in 190 BC), the resistance Turdetanas, Celtíberas or Lusitanas with Viriato at the head ...
These Celtic or Proto-Celtic peoples (Galaicos, Cantabrians, Astures, Belos, Titos and Pelendones, Arévacos, Vacceos, Celtíberos, Vettones, Carpetanos, Lusitanos) who, from the end of the Bronze Age and throughout the Iron Age, shared the culture of the Urn Fields - use of iron for weapons and cremation of their dead -, beliefs, gods, cults, magic, forests, devotion to ritual warfare and duels, resisted - fighting and defending in its fortified Castros - until the Roman Empire put an end to the Spanish Celtic or Celtiberia by destroying the last Celtiberian bastion (Numancia).